ResNet 논문 정리
0.Abstract
이 논문에 ResNet은 152개의 layer로 구성되었고, ILSVRC 2015 ImageNet Dataset classification 부분에서 top-5 error 3.57%로 1위를 기록하였다.
또한 ImageNet Dataset뿐만이 아니라, CIFAR-10등 다양한 데이터셋에서도 좋은 성능을 내고 있다.
이는 전년도 우승 네트워크 구조인 GoogleNet의 22개의 layer보다 무려 8배나 더 깊은 네트워크를 만들어 성공시켰다는 점에서 딥러닝 역사에 한 획을 그은 논문으로 평가 받고 있다.
!!! tldr "레즈넷 핵심 이해"
- [X] `레즈넷의 우수성` : `더 깊은 네트워크 구축`
- [ ] `Degradation`:
- [ ] `Reformation`:
- [ ] `Identity mapping`:
- [ ] `네트워크 구조`:
- [ ] `실험 결과 이해`:
- [ ] `pytorch를 이용한 코드 구현`:1.Introduction
네트워크를 깊게 쌓으면 발생하는 문제로 가장 확연히 들어나는 두가지가 바로 overfitting 문제와 degradation 문제이다. 하지만, 이 논문에서 제시하는 문제는 이중 degradation 문제이다.
.png)
: name (from)
!!! success
왜냐하면 56 레이어 모델과 20 레이어 모델을 비교한 결과 테스트와 트레이닝 둘다의 에러율이 더 깊은 56 레이어 모델이 더 높았기 때문이다. 만약 이게 오버피팅의 문제였다면, 트레이닝에서는 더 깊은 56레이어의 에러율이 더 작고, 테스트에서만 56레이어의 에러가 더 높았어야 한다. 그런점으로 봤을때, 모델을 더 깊이 쌓았을때 해결되어야 하는 근본적인 문제중 하나는 degradation 문제이다. !!! note
degradation은 vanishing gradient 와 exploding gradient 문제를 합쳐서 이야기 한다. !!! tldr "레즈넷 핵심 이해"
- [X] `레즈넷의 우수성` : `더 깊은 네트워크 구축`
- [X] `Degradation`: `오버피팅과의 차이 파악`
- [ ] `Reformation`:
- [ ] `Identity mapping`:
- [ ] `네트워크 구조`:
- [ ] `실험 결과 이해`:
- [ ] `pytorch를 이용한 코드 구현`:2.Deep Residual Learning
그렇다면 이 논문에서는 어떻게 degradation 문제를 해결하고 있을까? 이 논문에서는 “Residual Learning Framework”를 도입하여 성능 저하 문제를 해결하고 있다. Residual learning을 통해서 optimize가 더 쉬워지고, accuracy가 더 높아진다는 두가지 장점이 있다.
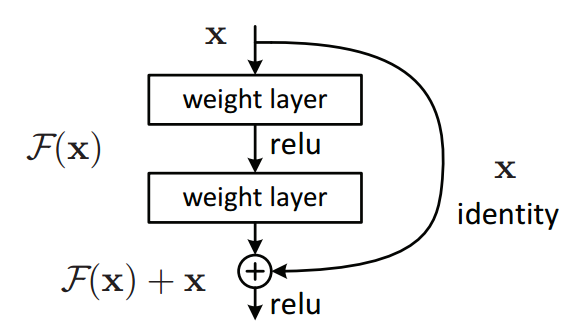
Reformation을 통해 레즈넷은 few stacked layer를 underlying mapping을 직접 학습하지 않고, residual mapping에 맞추어 학습하도록 한다. Reformation이란 H(x) = F(x) + x 에서 x를 이항하여 F(x)는 H(x)-x 라는 값으로 만드는 것을 의미 한다.
!!! success
underlying mapping 즉, 원래의 original mapping을 H(x)로 나타낸다면, residual mapping이 아닌 것은 H(x)를 처음부터 그 자체를 학습할 것이고, variance가 따러서 매우 클 것이겠지만,
residual learning 에서는 H(x) = F(x) + x 를 이용해서, stacked nonlinear layer의 mapping인 F(x)는 H(x)-x 를 학습하는 것이다. 이것을 통해서 F(x)는 0이 목표라는 특징을 가지기 때문에 variance는 매우 작아지고, optimize가 더 쉬워진다는 장점이 생긴다. original mapping은 F(x)+x 로 재구성 된다.!!! note
deep learning에서 에러율에는 variance가 영향을 끼치는 요소이다. variance가 크면,overfitting의 확률이 높아지고 모델 학습에 어려움이 생긴다. 반면 variance가 작으면,일반화에 도움이 된다. 하지만 무조건 이게 항상 맞는것이 아니다. 여기에 대해서 더 완전히 자세히 알고 싶다면,
bias-variance trade-off에 대해 공부해야하고, 아래 블로그의 그림들을 참조하라 :
[bias-variance trade-off](https://towardsdatascience.com/examples-of-bias-variance-tradeoff-in-deep-learning-6420476a20bd)Residual learning에서 알아야할 정말 중요한 단어중 하나가 바로 shortcut connection이라고도 불리는 identity mapping 이다.
!!! success
identity mapping을 통해서, 최소한 한쪽의 gradient는 계속 흐를 수 있게 mapping 해줌으로써 우리는 더 얕은 네트워크보다 최소한 더 나쁘지는 않은 결과를 보장 받을 수 있다.또, 이를 통해 vanishing gradient 와 exploding gradient 즉 degradation 문제를 해결할 수 있고, 모델을 더 깊게 쌓을 수 있게 되어서 결국 더 좋은 accuracy가 종종 나타난다. !!! tip
만약 위의 사진과 설명을 보았는데도 레즈넷이 아직도 완전히 이해가 가지 않는다면, 수식적으로 증명해 보는것을 추천한다. 그러면 완전히 머리 속으로 이 과정이 이해가 될것이다.
이 레즈넷 논문은 경험적으로 기술되었다. 이후에 이 레즈넷이 왜 효과가 있는지 설명한 후속 논문들이 많이 나와 있다. 원본을 읽고 싶다면, Identity Mappings in Deep Residual Networks 라는 논문을 읽으면 된다.
나는 빠르게 잘 이 논문을 정리해둔 블로그를 하나 추천해 주려고 한다. 첫번째 수식 증명을 잘 확인해보기를 바란다. [수식 관련 추천 논문](http://openresearch.ai/t/identity-mappings-in-deep-residual-networks/47) !!! tldr "레즈넷 핵심 이해"
- [X] `레즈넷의 우수성` : `더 깊은 네트워크 구축`
- [X] `Degradation`: `오버피팅과의 차이 파악`
- [X] `Reformation`: `easy to optimize`
- [X] `Identity mapping`: `increase accuracy`
- [ ] `네트워크 구조`:
- [ ] `실험 결과 이해`:
- [ ] `pytorch를 이용한 코드 구현`:3.Network Architecture
.png)
맨 왼쪽 부터 VGGnet, plain, residual 의 네트워크 구조 입니다.
Plain Network의 경우, 대부분 3*3 convolutional 필터로 이루어져있다.
여기는 룰이 두가지 있는데,
- 하나는 피쳐뱁과 같은 사이즈의 아웃풋일경우 레이어는 같은 개수의 필터를 가지게 하는것이다.
- 두번째로는 만약 피쳐맥 사이즈의 반이라면, 필터는 각 레이어 별 타임 컴플렉 시티를 맞추기 위해 필터의 개수를 두배로 늘린다.
- Downsampling 은 stride 2로 이루어지고, 마지막은 글로벌 에버리지 풀링을 적용하고, 1000-way fully connected layer에 softmax를 적용한다.
Residual Network의 경우, plain 모델에 shortcut connection을 추가한다. 같은 dimension일 경우 그냥 연결을 한다. 만약 Dimension이 증가할 경우, 두가지 방법을 사용 할 수 있다. Extral zero entries padded 를 주어 dimension을 증가 시키거나, 1*1convolutions을 이용해서 projection shortcut을 해주는 방법이 있다. 둘다 strided 2를 이용한다. 여기서 점선으로 된 부분은 dimension이 증가하는 부분이다.
ResNet 구현 세팅:
- image resized 224 * 224 (RC,HF)
- Batch normalization BN 사용
- Initialize Weights
- SGD, mini batch 256
- Learning rate 0.1 Iteration 60 * 10^4
- weight decay 0.0001, momentum 0.9
- No dropout
!!!success
Residual Network의 경우, plain 모델에 shortcut connection을 추가한다. !!! note
이 두 네트워크의 TOTAL FLOP은 3.6billion 입니다. 이건 VGG 는 19.6 billion FLOP이 있는데, 비교하면 18퍼센트 밖에 안되는 복잡성을 가지고 있다. !!! tip
실험적으로 이게 가장 좋아서 이렇게 네트워크 구조가 짜여졌다. 나처럼 이 네트워크 구조의 세팅이 왜 이렇게 이루어 졌고, 이게 가장 좋다는 것을 이해하기 어렵다면, 후속 논문들의 실험 내용과 증명을 보기를 추천한다. [identity mapping증명](http://openresearch.ai/t/identity-mappings-in-deep-residual-networks/47) !!! tldr "레즈넷 핵심 이해"
- [X] `레즈넷의 우수성` : `더 깊은 네트워크 구축`
- [X] `Degradation`: `오버피팅과의 차이 파악`
- [X] `Reformation`: `easy to optimize`
- [X] `Identity mapping`: `increase accuracy`
- [X] `네트워크 구조`: `plain network with identity mapping`
- [ ] `실험 결과 이해`:
- [ ] `pytorch를 이용한 코드 구현`:4.Experiment
.png)
: Table.2 학습 된 18-layer 및 34-layer plain/residual network의 validation data에 대한 10-crop testing 결과 중 top-1 error를 나타낸 표다.
분석결과:
- 34-layer ResNet이 18-layer ResNet보다 우수한 성능을 보인다. 즉, 깊은 네트워크에서 성능 저하 문제가 잘 해결되었다.
- plain network와 비교할때,residual learning의 유효성을 입증할 수 있다. (increase acurracy)
- 18-layer plain/residual network 간에는 유사한 성능을 보였지만, 논문의 Fig.4에 따르면 18-layer ResNet이 더욱 빠르게 수렴한다. 이는 network가 “not overly deep”한 경우(18-layers의 경우), 현재의 SGD solver는 여전히 plain net에서도 좋은 solution을 찾을 수 있다는 것으로 볼 수 있다.
- 하지만, 이러한 경우에도 ResNet에서는 빠른 수렴속도를 기대할 수 있다. (easy to optimize)
.png)
: Table.3 각 수치는 ImageNet validation data에 대한 10-crop testing error를 나타낸다.
분석결과:
- projection shortcut는 dimension을 늘릴 때만 사용되며, 다른 shortcut은 모두 identity로 세팅한다.
- ResNet152 즉, 가장 깊은 네트워크가 낮은 에러율을 보인다.
- 다른 네트워크에 비해 덜 복잡한 ResNet이 낮은 에러를 가진다. 즉, 레즈넷은 매우 훌륭한 네트워크이다.
위의 테이블의 결과에 따르면, A의 세팅은 zero-padding shortcut는 dimension matching에 사용되며, 모든 shortcut는 parameter-free이고, B의 세팅은 projection shortcut는 dimension을 늘릴 때만 사용되며, 다른 shortcut은 모두 identity이며, C의 세팅은 모든 shortcut은 projection이다.
!!! note
결과적으로는 C가 가장 좋지만, 그 차이가 아주 작다. 즉, 성능저하에 큰 영향을 주지 않는다. 하지만, C의 복잡성에 비해 B가 훨씬 덜 복잡하므로 논문에서는 B를 채택했다. .png)
Fig.5 ImageNet data에 대한 학습을 위한 deeper residual function F의 building block이다. 왼쪽은 Fig.3의 ResNet에서 feature map의 크기가 56x56인 경우의 building block이며, 오른쪽은 ResNet-50/101/152에서 같은 경우에 사용하는 ‘bottleneck’ building block이다.
다음으로 ImageNet dataset을 위한 deeper network를 설명한다. 감당할 수 없는 training time에 대한 우려로 인해, building block을 bottleneck design으로 수정한다. 각 residual function F, 2-layer stack대신 3-layer stack을 사용한다(Fig.5 참조). 3개의 layer는 각각 순서대로 1x1, 3x3, 1x1 conv layer이며, 1x1 conv layer는 dimension을 줄이거나 늘리는 용도로 사용하며, 3x3 layer의 input/output의 dimension을 줄인 bottleneck으로 둔다. Fig.5에서는 2-layer stack과 3-layer stack의 디자인을 보여준다. 둘은 유사한 time complexity를 갖는다.
여기서 parameter-free인 ideneity shortcut은 이 architecture에서 특히 중요하다. 만약 Fig.5의 오른쪽 다이어그램에서 identity shortcut이 projection으로 대체된다면, shortcut이 두 개의 high-dimensional 출력과 연결되므로 time complexity와 model size가 두 배로 늘어난다. 따라서 identity shortcut은 이 bottleneck design을 보다 효율적인 모델로 만들어준다.
CIFAR10 and Analysis:
^^결론만 말하자면, ImageNet Dataset이 아닌 다른 데이터 셋에서도 레즈넷은 잘 동작한다.^^ 또 overfitting이 조금 이루어지기는 했지만, 그래도 꽤 좋은 결과로 1000 레이어 까지 쌓아본 실험결과가 담겨져 있다. 작은 데이터셋에는 1000레이어가 오버피팅이 일어나지만, 큰 데이터셋을 대상으로는 좋은 결과를 받을것으로 예측되며, 레즈넷 덕분에 네트워크를 아주 깊게 구축 할 수 있게 되었다.
!!! info
좀더 자세히 분석하고 싶다면, [더 많은 실험결과](https://sike6054.github.io/blog/paper/first-post/)!!! tldr "레즈넷 핵심 이해"
- [X] `레즈넷의 우수성` : `더 깊은 네트워크 구축`
- [X] `Degradation`: `오버피팅과의 차이 파악`
- [X] `Reformation`: `easy to optimize`
- [X] `Identity mapping`: `increase accuracy`
- [X] `네트워크 구조`: `plain network with identity mapping`
- [X] `실험 결과 이해`: `많은 데이터 셋에 관해 더 깊은 네트워크 구축으로 높은 accuracy 성공`
- [ ] `pytorch를 이용한 코드 구현`:5.Pytorch를 이용한 코드 구현
class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
expansion = 1
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None, groups=1,
base_width=64, dilation=1, norm_layer=None):
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
if norm_layer is None:
norm_layer = nn.BatchNorm2d
if groups != 1 or base_width != 64:
raise ValueError('BasicBlock only supports groups=1 and base_width=64')
if dilation > 1:
raise NotImplementedError("Dilation > 1 not supported in BasicBlock")
# Both self.conv1 and self.downsample layers downsample the input when stride != 1
self.conv1 = conv3x3(inplanes, planes, stride)
self.bn1 = norm_layer(planes)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.conv2 = conv3x3(planes, planes)
self.bn2 = norm_layer(planes)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out
- 4:
- init 함수 안에서 3*3 컨볼루션 2개를 통과하는것을 확인하면, 이게 basic 구조라는것을 좀더 명확하게 볼 수 있다.
- 22:
- 또 forward 함수에서 identity mapping을 실제로 out += identity에서 더해주고 해주고 있음을 확인하자.
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
# Bottleneck in torchvision places the stride for downsampling at 3x3 convolution(self.conv2)
# while original implementation places the stride at the first 1x1 convolution(self.conv1)
# according to "Deep residual learning for image recognition"https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385.
# This variant is also known as ResNet V1.5 and improves accuracy according to
# https://ngc.nvidia.com/catalog/model-scripts/nvidia:resnet_50_v1_5_for_pytorch.
expansion = 4
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None, groups=1,
base_width=64, dilation=1, norm_layer=None):
super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()
if norm_layer is None:
norm_layer = nn.BatchNorm2d
width = int(planes * (base_width / 64.)) * groups
# Both self.conv2 and self.downsample layers downsample the input when stride != 1
self.conv1 = conv1x1(inplanes, width)
self.bn1 = norm_layer(width)
self.conv2 = conv3x3(width, width, stride, groups, dilation)
self.bn2 = norm_layer(width)
self.conv3 = conv1x1(width, planes * self.expansion)
self.bn3 = norm_layer(planes * self.expansion)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv3(out)
out = self.bn3(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out
!!! tip
init 함수에서 1*1 convolutional network 통과후 3*3 convolutional network 통과후 1*1 convolutional network를 통과하게 구조가 짜져있음을 확인하다.
역시 처럼 identity mapping이 있고, 그것을 더해줌을 확인하자. def _forward_impl(self, x):
# See note [TorchScript super()]
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.maxpool(x)
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.fc(x)
return x!!! tip
이 forward함수는 ResNet 클래스에서 가져온 것이다. forward 의 실제 구조가 아까 network architecture를 설명할때 보여줬던 사진의 구조와 같은지 한번 확인해보자. 마지막은 역시 논문에서 나온것처럼 global average pooling 과 linear projection, 그리고 softmax 함수를 적용한다. def resnet18(pretrained=False, progress=True, **kwargs):
r"""ResNet-18 model from
`"Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition" <https://arxiv.org/pdf/1512.03385.pdf>`_
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
progress (bool): If True, displays a progress bar of the download to stderr
"""
return _resnet('resnet18', BasicBlock, [2, 2, 2, 2], pretrained, progress,
**kwargs)!!! tip
실제로 논문에서 나온것 처럼, 레즈넷 18과 34는 basic block을 사용한다. def resnet50(pretrained=False, progress=True, **kwargs):
r"""ResNet-50 model from
`"Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition" <https://arxiv.org/pdf/1512.03385.pdf>`_
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
progress (bool): If True, displays a progress bar of the download to stderr
"""
return _resnet('resnet50', Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3], pretrained, progress,
**kwargs)
!! tip
반면, 레즈넷 50이상은 실제로 논문에서 나온것 처럼, bottleneck구조를 이용해서 구현한것을 확인할 수 있다. !!! success
만약 파이토치 내부 레즈넷 구현이 좀 더 궁금해서 코드 전문을 보고싶다면 아래를 클릭해라.
>[파이토치 ResNet구현 코드](https://github.com/pytorch/vision/blob/master/torchvision/models/resnet.py)!!! tldr "레즈넷 핵심 이해"
- [X] `레즈넷의 우수성` : `더 깊은 네트워크 구축`
- [X] `Degradation`: `오버피팅과의 차이 파악`
- [X] `Reformation`: `easy to optimize`
- [X] `Identity mapping`: `increase accuracy`
- [X] `네트워크 구조`: `plain network with identity mapping`
- [X] `실험 결과 이해`: `많은 데이터 셋에 관해 더 깊은 네트워크 구축으로 높은 accuracy 성공`
- [X] `pytorch를 이용한 코드 구현`: `코드 구조 이해`!!! sucess "레즈넷 이해 완료"
수고하셨습니다 :)'딥러닝 논문정리' 카테고리의 다른 글
| FastSpeech1, 2 (0) | 2021.07.08 |
|---|---|
| Transformer TTS (0) | 2021.07.08 |
| [3]Encoder-Decoder TTS_2 (0) | 2021.07.08 |
| [2]Encoder-Decoder TTS_1 (0) | 2021.07.08 |
| [1]Introduction to Speech Preprocessing (0) | 2021.07.08 |
